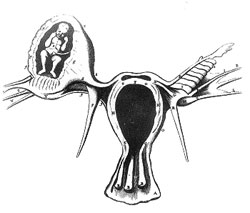
 An ectopic pregnancy is a problematic situation of pregnancy. Here, the fetus’s development occurs outside the womb, mostly in the Fallopian tube. Such a complicated situation arises in 1 percent of the cases of childbirth. It can cause severe internal bleeding due to the rupturing of the blood vessels due to the fetus’s growth. It gravely endangers the life of the mother.
An ectopic pregnancy is a problematic situation of pregnancy. Here, the fetus’s development occurs outside the womb, mostly in the Fallopian tube. Such a complicated situation arises in 1 percent of the cases of childbirth. It can cause severe internal bleeding due to the rupturing of the blood vessels due to the fetus’s growth. It gravely endangers the life of the mother.
Despite medical advancement in the early detection of this condition, ectopic pregnancy is a potential medical emergency, and non-commencement of treatment on time can lead to death.
Treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy
When detected early, this condition can be treated by the intake of the drug methotrexate. It stops any further development of the embryo. The procedure of abortion can then remove the fetus. The remaining tissues either get reabsorbed into the woman’s body or emerge during menstrual.
In case of internal bleeding, it is necessary to carry out the surgery. But, the final decision to go ahead with the procedure is a challenging one to take. This is because the detection technique of ultrasound does not provide enough evidence of any blood clot in the Fallopian tube region. The most common complication of internal bleeding is severe blood loss to the extent that the heart finds it difficult to pump sufficient oxygenated blood all over the body. This condition is technically known as hypovolaemic shock.
The surgical procedure of Laparotomy involves cutting the skin in the abdominal wall. In this way, the surgical instruments can access the affected Fallopian tube. It is then either cut to remove the growing embryo or wholly removed.
The patient’s follow-up after surgery is very well in developed countries. However, the prognosis is inferior in developing countries of Africa, where the mortality rates of mothers are very high.
Treating this type of pregnancy plays a vital role in deciding women’s future fertility. Compared with surgical intervention, intake of methotrexate as treatment can lead to a normal pregnancy, with the next embryo’s growth in the uterus.
A salpingostomy is a surgical cut made into a Fallopian tube. A salpingectomy is the complete removal of this organ. However, the fertility rate will be higher the next time the former method is chosen earlier.
There is also the increasing use of minimal-access or ‘keyhole’ surgery to deal with ectopic pregnancy, whether to remove the tube or to open the tube and remove the ectopic pregnancy alone. Keyhole surgery, being less invasive, allows a faster recovery and shorter time in hospital than conventional surgery and might reduce the risk of a further ectopic pregnancy. Where the tube has ruptured and bleeding into the abdomen, immediate surgery is required, and the tube is removed together with the pregnancy.
Is surgery always necessary?
Sometimes, ectopic pregnancy will not require any surgery. If you are clinically stable and at a very early stage in pregnancy with a small, unruptured ectopic pregnancy, then sometimes doctors will simply monitor you to determine whether any specific treatment is necessary. This is because some early ectopic pregnancies may end without leading to hemorrhage or tubal rupture. Doctors use a combination of ultrasound scans and serial measurements of hCG to monitor ectopic pregnancies. Treatment with drugs to stop the pregnancy growing is also being explored as an alternative to surgery.
The commencement of early treatment of this condition is closely related to the identification of the signs and symptoms of it. Unfortunately, these indicators remain absent or subtle in the early stages. Only prior awareness of them by the woman or her family members can prove extremely handy.
Some of the early stage signs and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy are lower abdomen pain, inflammation, mild discomfort, pain while urinating, and pain while having a bowel movement. In the later stages, the severity of bleeding intensifies.
The signs of this condition can also remain undetected owing to their similarities with the ailments like appendicitis, urinary system complaints, pelvic inflammatory diseases, gastrointestinal disorders, and gynecologic problems. In this way, the starting of an early treatment can get delayed.
